Understanding Kaizen & Continuous Improvement in Lean Manufacturing
The history of Kaizen, or Kaizen Blitz, is well-documented. The inventor of Kaizen, Masaaki Imai, was a managerial theorist and consultant on the Toyota production system. In 1986, he wrote a book titled “Kaizen: The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success.” His book outlined his examination of manufacturing processes over a decades-long career.
The word Kaizen breaks down into two parts: the first, “Kai,” translates to “change.” The second part, “Zen,” translates to “for the better.” Put them together, “change for the better.”
Below, we’ll take a deep dive into Imai’s concept of Kaizen. We will discuss how it changed the business world and led to lean manufacturing and continuous improvement practices.
What Is Kaizen?
Kaizen is both a mindset and a methodology focused on achieving small, incremental changes that lead to lasting improvement. Rather than relying on one major breakthrough, Kaizen emphasizes ongoing progress, teamwork, and problem-solving to strengthen operations over time.
Kaizen & Continuous Improvement
At its core, Kaizen embodies the principle of continuous improvement. This means regularly evaluating processes, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing adjustments that add value. Continuous improvement isn’t limited to large-scale projects—it thrives on daily, small changes made by everyone in the organization. Over time, these refinements compound into significant gains in productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Kaizen & Lean Manufacturing
Kaizen plays a central role in the foundation of lean manufacturing. Lean focuses on eliminating waste and maximizing value, and Kaizen provides the practical approach to make that possible. Through Kaizen, teams learn to streamline workflows, minimize downtime, and improve resource efficiency. By combining lean principles with a Kaizen mindset, organizations create a culture of accountability and adaptability that drives long-term success.
What Are the 5 Principles of Kaizen?
Kaizen consists of five core principles. Together, these five specific areas empower organizations to implement impactful solutions that elevate productivity and customer satisfaction.
1. Know Your Customer
Before selling to them, identify their needs and problems to make your product more valuable to them.
2. Let It Flow
Pursue the elimination of waste, waste being anything that fails to add value.
3. Gemba Focus
Gemba focusmeans going to where the action happens, like factory floors, to understand the real situation. Managers should be present with frontline workers.
4. Be Transparent
Keep performance data out in the open for all to view key areas for improvement.
5. Empower People
Organize teams for success, providing clear goals for improving productivity, safety, and quality.
Kaizen operates as an action plan and a philosophical approach. The plan focuses on improving organization by optimizing floor layouts to reduce errors, downtime, and rework.
As a philosophy, Kaizen focuses on employee involvement. The philosophy suggests that employees play a vital role in the success of the company. Kaizen sees employees as important to overall success, not just cogs in a machine. Their actions and performance are key to achieving institutional goals.
What Are the Benefits of Kaizen?
A successful Kaizen process delivers a handful of benefits to institutional success, including:
Better Cost Control
Kaizen cuts costs by reducing waste, without hurting morale like pay cuts or layoffs do.
Reduce Waste
The goal of Kaizen is 100% efficiency, meaning processes that bring down waste in materials and time.
Strengthens Communication
Kaizen aims to break down silos and increase transparency and accountability, encouraging employees to help identify areas of improvement.
Better Quality Control
Kaizen uses data analysis to find problems early, improving quality and making customers happier.
What Is a Just-in-Time Inventory Strategy?
Introducing a just-in-time inventory is one of the specific types of Kaizen that eliminates waste dramatically.
It begins with stream mapping, which analyzes the flows of materials from beginning to end. The maps serve as a visual guide, illustrating each stage of a product’s lifecycle. From there, managers can optimize the process by introducing a just-in-time inventory if applicable.
A just-in-time inventory aligns orders of raw materials with suppliers and production schedules. The outcome is a flow of materials that come when needed, reducing the need for extra storage space.
Advantages of just-in-time inventory are less waste, strong supplier relationships, and quicker production.
What Is the Kaizen 5s Framework?
Kaizen is about identifying and solving problems that lead to continuous improvement. However, this requires standardization of practices. So, with any Kaizen initiative, management must follow these five steps:
1. Sort
Organize tools, parts, and materials into two groups: needed and not needed; get rid of anything not needed.
2. Straighten
Get everything ready before starting production to avoid mistakes or delays. Organize parts, materials, and workers for efficiency.
3. Shine
Clean and inspect all equipment and workstations to reduce errors and malfunctions.
4. Standardize
Create written guidelines and procedures for each stage of the process, including steps, responsibilities, and communication hierarchies.
5. Sustain
Repeat the first four steps to maintain peak product quality and efficient workflows.
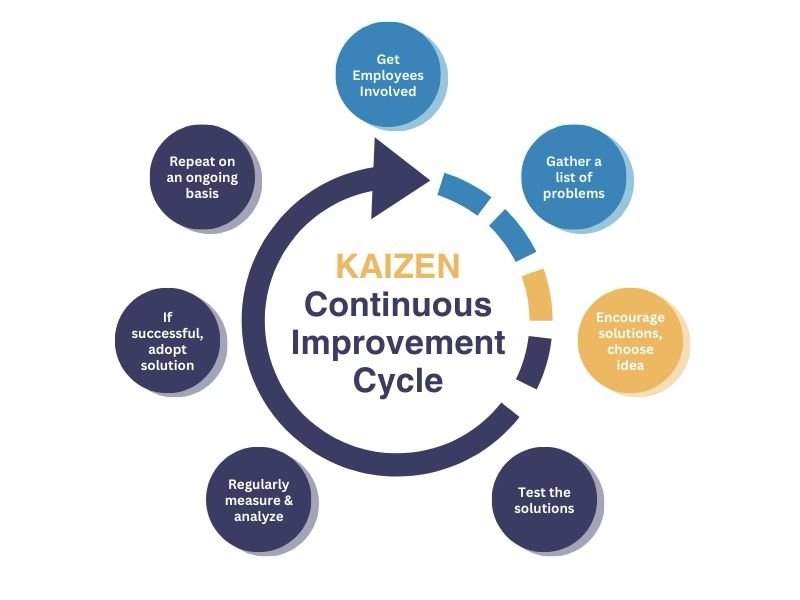
What Is an Example of a Kaizen Event?
A prime example of a Kaizen event would be a company looking to reduce product completion times.
For example, say a car manufacturer wants to improve the speed at which they build and ship one of their cars. The Kaizen process would look something like this:
- Set goals by defining KPIs at each stage, such as reducing process cycle time or inventory stockouts.
- Study current processes to find inefficiencies, like broken equipment or departments with lots of downtime.
- Strategize and implement improvements, such as scheduling routine employee training or creating just-in-time inventory schedules.
- Check progress every day, see if changes work, and report results to make sure they fix problems and meet goals.
- Standardize all practices that work, creating written and visual guides for new workflows.
- If the changes don’t work, begin again with new information in mind.
What Is the Kaizen PDCA Cycle?
A standard way to practice Kaizen is by following the process of plan, do, check, and act (PDCA). In essence, PDCA incorporates the scientific method into every Kaizen event. It works as follows:
- Plan: Establish goals and what’s necessary to reach them
- Do: Put change into motion
- Check: Evaluate performance results of the new changes
- Act: Standardize changes or begin again, depending on the outcome
Kaizen FAQs
What does Kaizen mean?
Kaizen is all about continuous improvement. It’s a business philosophy that focuses on making small, ongoing changes that drive efficiency, quality, and employee engagement over time.
What does Kaizen mean in Japanese?
In Japanese, “Kai” translates to “change,” and “Zen” means “for the better.” Together, Kaizen means “change for the better,” emphasizing progress through steady improvements.
How does Kaizen work?
Kaizen works by encouraging everyone in an organization to identify problems, suggest solutions, and implement small changes that improve processes. Over time, these incremental steps lead to significant performance gains.
How is Kaizen implemented?
Kaizen is implemented by setting clear goals, involving employees at all levels, and using structured tools like the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle. Companies often hold Kaizen events to focus efforts on solving specific challenges.
What is a Kaizen event?
A Kaizen event is a short, focused improvement workshop where a cross-functional team works on a specific process or problem. These events help deliver rapid results in a few days.
How long should a Kaizen event take?
Most Kaizen events last between three and five days. This timeframe allows enough focus to achieve measurable improvements while minimizing disruption to day-to-day operations.
Does Kaizen really work?
Yes. When properly implemented, Kaizen leads to measurable improvements in productivity, quality, communication, and cost reduction. Its success depends on consistent application and employee involvement.
How does Kaizen reduce cost?
Kaizen reduces cost by eliminating waste, improving workflow, and minimizing downtime. Rather than relying on layoffs or budget cuts, it improves efficiency to achieve savings without harming morale.
Is Kaizen Lean or Six Sigma?
Kaizen is a core part of Lean manufacturing, focusing on eliminating waste and maximizing value. It can also complement Six Sigma by supporting problem-solving and process improvement initiatives.
What companies use Kaizen?
Kaizen originated at Toyota but has since been adopted by companies worldwide. Its principles apply across industries.
What does it take to succeed at Kaizen?
Success with Kaizen requires leadership support, employee involvement, clear goals, and consistent follow-through. Building a culture of continuous improvement is the key to sustaining long-term results.
Drive Continuous Improvement with CAI Software Solutions
Implementing Kaizen effectively requires tools that simplify processes, improve communication, and support consistent execution across teams. With CAI’s software solutions, manufacturers can streamline operations, reduce waste, enhance quality, and build a culture of continuous improvement that sustains long-term growth.
Ready to strengthen your Kaizen initiatives? Contact CAI Software today to discover how our solutions can help your business achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and success.
